The History of Korea
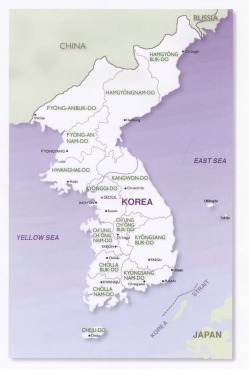
Map of Korea
Korea, one of the world’s oldest nations, also grew while being influenced by Chinese culture. Throughout their history, Korea adopted many Chinese ideas when it was needed, and changed them according to their standards. Korea is a peninsula on the Asian mainland, and connected to northern China. The boundary that separates them is a river called the Amnok River, or the Yalu River. Because of this, it was always easy for movement between China and Korea. Also, sometimes Chinese influences reached Japan from Korea, since they were close.
The first people to inhabit Korea were probably nomads traveling from the north. In 108 B.C., Korea was attacked by the Chinese, during the Han Dynasty. The Koreans fought back, and gained back most of their lost land. Over the next 700 years, Korea created three main kingdoms, which fought wars among themselves for more power over Korea. During the 600s, the Silla kingdom in the southeast gained power over the other two kingdoms, Goguryeo and Baekje, and controlled Korea, and forced out the Chinese still living there. Korea was finally united, for the first time. Actually, the Goguryeo and Bakjae kingdoms had seemed much more powerful than Silla, especially Goguryeo. After Silla won the war, Silla nobles soon began to fight amongst themselves for more power, and peasants began to rebel. This lasted until 935, when Silla fell from power. The great unified kingdom Silla had built fell apart and gave way to the Later Three Kingdoms period that lasted from 892 to 963. Then, Koryo, another kingdom, ruled in 918 to 1392. Korea’s name comes from Koryo. During this time, a civil service was developed, and Buddhism became popular.
Korea continued to develop, but gained some influences from China, like how to make pottery, and two belief systems: Confucianism, and Buddhism. Korea eventually became known for the beautiful pottery that has a bluish-green glaze, called celadon. The way Japan learned Buddhism was from Korea, because Korea is so close to Japan.
Korea struggled to remain independent from foreign countries. In the 1200s, when China was conquered by the Mongols, Korea was also controlled until the Mongols lost power in the late 1300s. In 1392, the wealthy and powerful Yi family formed the Choson Dynasty in Korea, and drove back a Japanese army in the late 1500s. The Choson Dynasty lasted for a long 500 years.
The first people to inhabit Korea were probably nomads traveling from the north. In 108 B.C., Korea was attacked by the Chinese, during the Han Dynasty. The Koreans fought back, and gained back most of their lost land. Over the next 700 years, Korea created three main kingdoms, which fought wars among themselves for more power over Korea. During the 600s, the Silla kingdom in the southeast gained power over the other two kingdoms, Goguryeo and Baekje, and controlled Korea, and forced out the Chinese still living there. Korea was finally united, for the first time. Actually, the Goguryeo and Bakjae kingdoms had seemed much more powerful than Silla, especially Goguryeo. After Silla won the war, Silla nobles soon began to fight amongst themselves for more power, and peasants began to rebel. This lasted until 935, when Silla fell from power. The great unified kingdom Silla had built fell apart and gave way to the Later Three Kingdoms period that lasted from 892 to 963. Then, Koryo, another kingdom, ruled in 918 to 1392. Korea’s name comes from Koryo. During this time, a civil service was developed, and Buddhism became popular.
Korea continued to develop, but gained some influences from China, like how to make pottery, and two belief systems: Confucianism, and Buddhism. Korea eventually became known for the beautiful pottery that has a bluish-green glaze, called celadon. The way Japan learned Buddhism was from Korea, because Korea is so close to Japan.
Korea struggled to remain independent from foreign countries. In the 1200s, when China was conquered by the Mongols, Korea was also controlled until the Mongols lost power in the late 1300s. In 1392, the wealthy and powerful Yi family formed the Choson Dynasty in Korea, and drove back a Japanese army in the late 1500s. The Choson Dynasty lasted for a long 500 years.
The History of the Khmer Empire
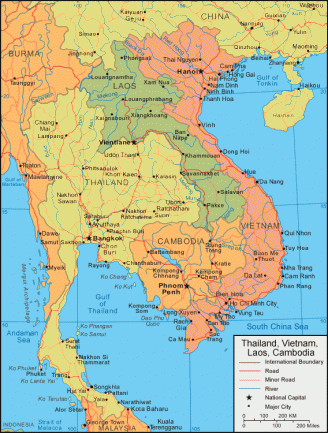
Map of Vietnam
Vietnam is located on the eastern part of the Indochina peninsula in Southeast Asia. They broke off of Chinese rule in the 900s. The Chinese had conquered the land that is now known as Vietnam, in 111 B.C. Vietnam was called Nam Viet at the time. China’s rule was peaceful in the beginning, because they mostly wanted to utilize the convenient ports overlooking the South China Sea. However, the Chinese began to force the Vietnamese to take on Chinese culture. They required everyone to wear Chinese clothing, and speak in Chinese. They also were told to practice Confucianism and Buddhism, even though many tried to resist.
In A.D. 40, the husband of a noblewoman by the name of Trung Trac, was killed by the Chinese. Trung Tac and her sister, Trung Nhi, both led a rebellion against China’s government. They were at first successful, but started to get overpowered (from China’s vast forces). Finally, in the 900s, when the Tang Dynasty weakened, the Vietnamese won their freedom. However, the Vietnamese had adopted some principles of Confucianism and Buddhism.
In 939, Dai Vet, was created. Dai Vet was an independent kingdom, and in the 1200s, was attacked by the Mongols who had conquered China. After three brave battles, where the Vietnamese drove back the Mongolian forces, the kingdom was left a weak shell of what it had been. However, in 1407, when Chinese soldiers from the Ming Dynasty invaded, the Vietnamese won, and forced them out, in 1428. Dai Vet then resumed its way of independency, and ruled themselves. When Dai Vet conquered Champa, an enemy kingdom to the south, they gained back their power.
There are many wonderful legends about the development of Vietnam. One of the legends was about a Vietnamese prince, by the name of Lac Long Quan, who came to the northern part of Nam Viet, and married a beautiful princess, who was from the mountains, and was called Au Co. She was also the wife of a supposedly Chinese man, who came from the north. However, Lac Long Quan and Au Co married, on the peak of Mount Tan Vien, and had 100 children, all of them young males, who were to make up half of the Vietnamese people. Because Lac Long Quan and Au Co could not stay together, due to their different ancestries, Au Co brought half the men over the northern mountains, and became the great ancestors of the Muong people. The remaining half followed Lac Long Quan to what is now Vietnam. The Vietnamese consider Au Co and Lac Long Quan their ancestors. This legend leads us to believe that the Vietnamese had come from the Malay-Polynesian people that lied very near the sea, and had met and conversed with the Mongolians, who live in the Southern China plains.
In A.D. 40, the husband of a noblewoman by the name of Trung Trac, was killed by the Chinese. Trung Tac and her sister, Trung Nhi, both led a rebellion against China’s government. They were at first successful, but started to get overpowered (from China’s vast forces). Finally, in the 900s, when the Tang Dynasty weakened, the Vietnamese won their freedom. However, the Vietnamese had adopted some principles of Confucianism and Buddhism.
In 939, Dai Vet, was created. Dai Vet was an independent kingdom, and in the 1200s, was attacked by the Mongols who had conquered China. After three brave battles, where the Vietnamese drove back the Mongolian forces, the kingdom was left a weak shell of what it had been. However, in 1407, when Chinese soldiers from the Ming Dynasty invaded, the Vietnamese won, and forced them out, in 1428. Dai Vet then resumed its way of independency, and ruled themselves. When Dai Vet conquered Champa, an enemy kingdom to the south, they gained back their power.
There are many wonderful legends about the development of Vietnam. One of the legends was about a Vietnamese prince, by the name of Lac Long Quan, who came to the northern part of Nam Viet, and married a beautiful princess, who was from the mountains, and was called Au Co. She was also the wife of a supposedly Chinese man, who came from the north. However, Lac Long Quan and Au Co married, on the peak of Mount Tan Vien, and had 100 children, all of them young males, who were to make up half of the Vietnamese people. Because Lac Long Quan and Au Co could not stay together, due to their different ancestries, Au Co brought half the men over the northern mountains, and became the great ancestors of the Muong people. The remaining half followed Lac Long Quan to what is now Vietnam. The Vietnamese consider Au Co and Lac Long Quan their ancestors. This legend leads us to believe that the Vietnamese had come from the Malay-Polynesian people that lied very near the sea, and had met and conversed with the Mongolians, who live in the Southern China plains.
The History of the Khmer Empire
The Khmer Empire dominated the other kingdoms on the mainland of Southeast Asia, and lasted very long, from the 500s to 1431, when they fell to the Thais. It is in the center of what is today is Cambodia. The peak of the Khmer empire was in the 1200s, and overshadowed any other civilization on the southern section of the southeastern part of the Asian peninsula.
Khmer’s culture was heavily influenced by both India and China. For example, Khmer got its method of rice farming from China, and religions from India, like Hinduism and Buddhism, from India.
One of the factors of Khmer’s prosperity was their abundance of rice. Peasant farmers built well-planned irrigation systems, which greatly helped the rice to grow. These irrigation systems were a huge complex of waterways and canals, to allow the water to flow where it was needed. Most of the Khmer Empire’s water came from the multitude of monsoons that came yearly. Later, the Khmers developed a new kind of rice seed, which allowed them three harvests a year.
From India, the Khmers borrowed many aspects from India too, like the writing system, an all-powerful god, also known as a god-king, and two religions, Buddhism and Hinduism.
The Khmer ruler started to build a new capital at Angkor, in the late 800s. Angkor was immense; it was twice as large as Manhattan today. It was a huge complex of gorgeous buildings and temples, the most famous known as Angkor Wat, built in the 1100s. It is still standing today, nearly covering one full square mile, and is the largest religious structure today, and considered by some the most beautiful. The temples had honored one god, Vishnu, but now there are several Buddhist statues that were added later. Some carvings in the magnificent temple are actually of daily life.
After the emperor of the Khmer Empire, Jayavarman VII, died in approximately 1215, Angkor fell into terror, and became very weak, enough for the Siamese to invade. The citizens fled, and Angkor fell into war many times, becoming a city full of chaos. Unfortunately, some of Angkor Wat’s beautiful relics were destroyed during this time. However, Angkor Wat has still retained its beauty.
Khmer’s culture was heavily influenced by both India and China. For example, Khmer got its method of rice farming from China, and religions from India, like Hinduism and Buddhism, from India.
One of the factors of Khmer’s prosperity was their abundance of rice. Peasant farmers built well-planned irrigation systems, which greatly helped the rice to grow. These irrigation systems were a huge complex of waterways and canals, to allow the water to flow where it was needed. Most of the Khmer Empire’s water came from the multitude of monsoons that came yearly. Later, the Khmers developed a new kind of rice seed, which allowed them three harvests a year.
From India, the Khmers borrowed many aspects from India too, like the writing system, an all-powerful god, also known as a god-king, and two religions, Buddhism and Hinduism.
The Khmer ruler started to build a new capital at Angkor, in the late 800s. Angkor was immense; it was twice as large as Manhattan today. It was a huge complex of gorgeous buildings and temples, the most famous known as Angkor Wat, built in the 1100s. It is still standing today, nearly covering one full square mile, and is the largest religious structure today, and considered by some the most beautiful. The temples had honored one god, Vishnu, but now there are several Buddhist statues that were added later. Some carvings in the magnificent temple are actually of daily life.
After the emperor of the Khmer Empire, Jayavarman VII, died in approximately 1215, Angkor fell into terror, and became very weak, enough for the Siamese to invade. The citizens fled, and Angkor fell into war many times, becoming a city full of chaos. Unfortunately, some of Angkor Wat’s beautiful relics were destroyed during this time. However, Angkor Wat has still retained its beauty.
The History of the Khmer Empire
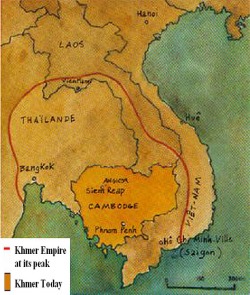
Map of the Khmer Empire
The Khmer Empire dominated the other kingdoms on the mainland of Southeast Asia, and lasted very long, from the 500s to 1431, when they fell to the Thais. It is in the center of what is today is Cambodia. The peak of the Khmer empire was in the 1200s, and overshadowed any other civilization on the southern section of the southeastern part of the Asian peninsula.Khmer’s culture was heavily influenced by both India and China. For example, Khmer got its method of rice farming from China, and religions from India, like Hinduism and Buddhism, from India.One of the factors of Khmer’s prosperity was their abundance of rice. Peasant farmers built well-planned irrigation systems, which greatly helped the rice to grow. These irrigation systems were a huge complex of waterways and canals, to allow the water to flow where it was needed. Most of the Khmer Empire’s water came from the multitude of monsoons that came yearly. Later, the Khmers developed a new kind of rice seed, which allowed them three harvests a year.From India, the Khmers borrowed many aspects from India too, like the writing system, an all-powerful god, also known as a god-king, and two religions, Buddhism and Hinduism.The Khmer ruler started to build a new capital at Angkor, in the late 800s. Angkor was immense; it was twice as large as Manhattan today. It was a huge complex of gorgeous buildings and temples, the most famous known as Angkor Wat, built in the 1100s. It is still standing today, nearly covering one full square mile, and is the largest religious structure today, and considered by some the most beautiful. The temples had honored one god, Vishnu, but now there are several Buddhist statues that were added later. Some carvings in the magnificent temple are actually of daily life.After the emperor of the Khmer Empire, Jayavarman VII, died in approximately 1215, Angkor fell into terror, and became very weak, enough for the Siamese to invade. The citizens fled, and Angkor fell into war many times, becoming a city full of chaos. Unfortunately, some of Angkor Wat’s beautiful relics were destroyed during this time. However, Angkor Wat has still retained its beauty.








